Digital Analytics is a science that systematically analyzes internet data to enhance an organization’s ecosystem and improve business processes.
Unlike Web Analytics, which primarily focuses on web data, Digital Analytics can include many data sources, including websites, mobile apps, social media platforms, third-party data, marketing data, sales data, IoT device data, and CRM data. When combined correctly, this data leads to smarter marketing and business decisions, both online and offline.
The ultimate objective of Digital Analytics is to gain a comprehensive understanding of the effectiveness of current strategies so resources can be aligned to enable rapid business growth and to identify and eliminate strategies and processes that are not yielding desirable results.
DA vs. Experience, Assumptions & Faith
In today’s dynamic business and digital landscapes, relying solely on experience, assumptions, and faith is imprudent.
Experience
While experience is undoubtedly valuable, it doesn’t scale efficiently. The wisdom gained from years of practice cannot be instantaneously transferred or made applicable to every new situation in an ever-changing environment.
Assumptions
Similarly, assumptions, despite their plausibility, have their limitations. They are typically based on past experiences or patterns and may not accurately predict the trajectory of rapidly evolving digital trends within a fast-paced digital landscape.
Faith
Faith, while a powerful motivator, is susceptible to biases and subjective interpretations. It can cloud judgment and lead to decisions that are not entirely based on facts or current realities.
Digital Analytics
Digital analytics provides an objective perspective, unlike experience, assumptions or faith.
It uses data gathered from various digital touchpoints to create a clear picture of the present and more accurately predicts future trends.
Consequently, while experience, assumptions, and faith play their roles in decision-making, digital analytics should complement them to achieve a more comprehensive and accurate understanding needed to achieve rapid business growth goals.
The 3 Elements of Digital Analytics
Digital analytics relies on three essential elements: data, context, and creativity. Each of these elements plays a unique role in extracting nuanced insights.
Data
The success of analytics is all about the quality of the data, which can be sourced from various channels.
Online data, including website traffic, social media engagement, and user behavior, provides valuable insights into digital interactions.
On the other hand, offline data, derived from physical interactions and sales transactions, offers a comprehensive view by bridging the gap between the digital and tangible worlds.
The analysis can be further enriched by incorporating quantitative data, such as numerical metrics, and qualitative data, including customer feedback and sentiment analysis.
Both internal sources, such as proprietary databases, and external sources, like market research reports, can also be utilized to enhance the data landscape.
High-quality datasets are a crucial source and a competitive advantage for companies.
They provide valuable insights for strategic decision-making. These datasets are carefully curated and diverse, empowering organizations to anticipate market trends, optimize operations, and enhance customer experiences.
Possessing accurate and up-to-date information enables companies to stay agile and innovative, setting them apart in the competitive business landscape where AI data-driven strategies are essential.
Context
Context is an essential aspect of data interpretation that is crucial in providing a comprehensive understanding of the data.
It involves analyzing the circumstances and conditions surrounding the data’s creation, both internal and external, to gain a deeper insight into its meaning and significance.
The contextual lens extends beyond the data itself and encompasses market dynamics, industry trends, and organizational goals.
By considering these factors, analysts can identify patterns and trends that may not be immediately apparent from the data alone.
For instance, understanding the market dynamics can help analysts identify the factors that are driving the data trends and predict future outcomes.
Similarly, analyzing industry trends can provide insights into the competitive landscape and help organizations stay ahead of the curve.
Moreover, the context is crucial in identifying problems or opportunities within the data and for steering analysis towards actionable insights.
Context is a critical pillar of data interpretation that provides the necessary background information for understanding the data.
Context aids Analysts in gaining deeper insights, identifying patterns, and developing actionable insights that drive business success.
Creativity
Creativity is the third element that adds an inventive dimension to the analytical process.
It involves thinking beyond conventional methods to uncover unique solutions and patterns within the data.
Creative analytics may involve:
-
- Exploring novel correlations.
- Experimenting with different data visualization techniques.
- Devising innovative strategies based on the insights gleaned.
This creative approach is crucial in tackling complex problems or seizing uncharted growth opportunities.
Combining these three key elements can transform a digital analytics program from a simple data analysis tool to a powerful prescriptive analytics decision-making business success tool.
Types of Digital Analytics
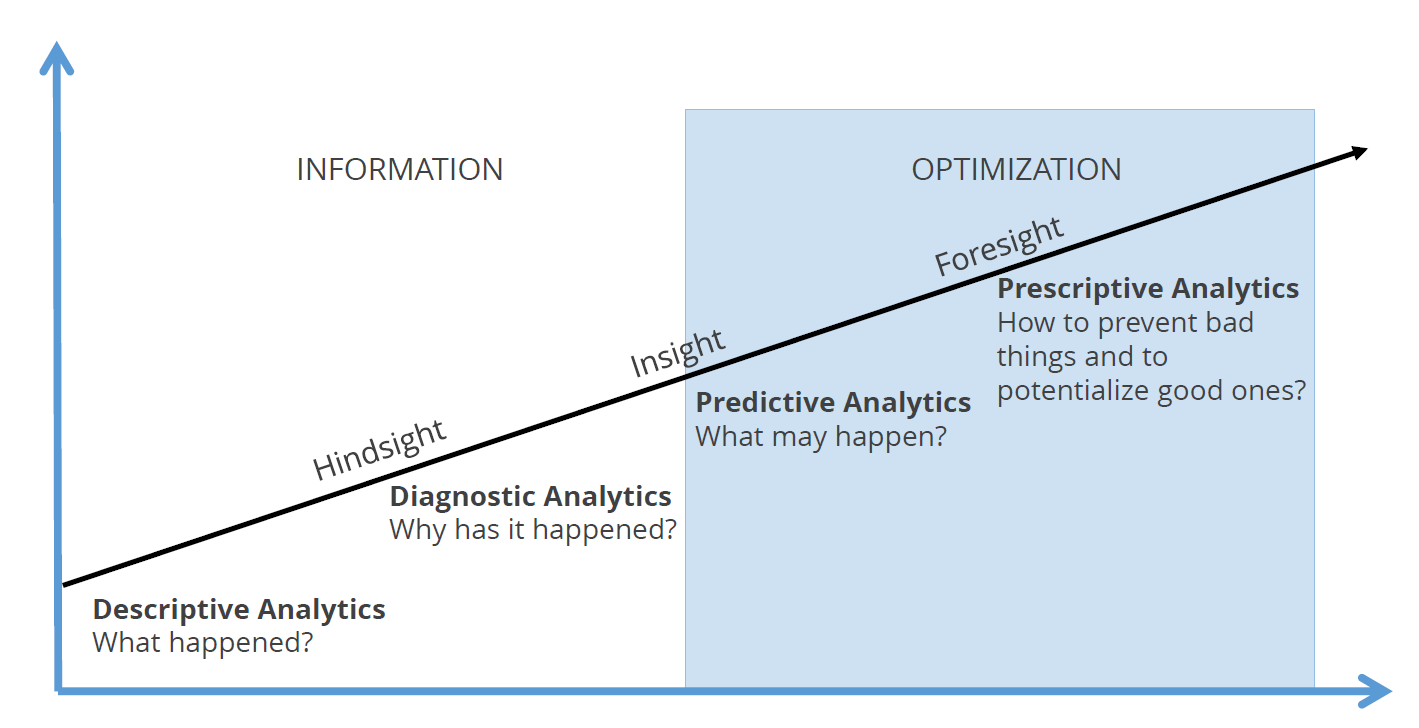
There are four levels of digital analytics, each with a specific role in analyzing complex data.
Descriptive (The What) – Click Stream
Descriptive analytics, also known as click-stream analysis, is a type of analysis that focuses on describing what happened in the past. It provides a basic understanding of past events and helps to identify patterns and trends.
Diagnostic (The Why)
Diagnostic analytics answers the question “why” things happen and is a powerful tool that helps to identify the underlying reasons behind certain events or occurrences. By asking the question ‘why’ something happened, it delves deeper into the data to uncover the good and bad root causes. This information can then be used to make informed decisions and take appropriate actions in the future.
Predictive (The What May)
Predictive analytics takes a forward-looking approach by exploring what may happen based on historical data patterns, enabling proactive decision-making.
Prescriptive (The Light)
Lastly, prescriptive analytics advises on preventing unfavorable outcomes and capitalizing on favorable ones.
It is essential for companies to progress from descriptive analytics to more advanced analytics programs to optimize their growth and profit margins.
While descriptive analytics provides a fundamental understanding of past performance, advanced analytics enables businesses to gain deeper insights into their operations and make more impactful data-driven decisions around operations, budget allocation, and growth opportunities.
Digital Analytics Maturity Model
Organizations frequently make the mistake of hastily adopting cutting-edge analytics solutions, resulting in unforeseen growth challenges.
Such a hurried approach toward implementing advanced analytics can lead to a plethora of issues that could potentially hamper the organization’s growth trajectory.
As analytics solutions become more sophisticated, businesses must exercise prudence and diligence in their decision-making process.
This will enable them to identify and mitigate potential growth challenges beforehand and ensure that their analytical capabilities are deployed in a manner that is both sustainable and beneficial to the organization.
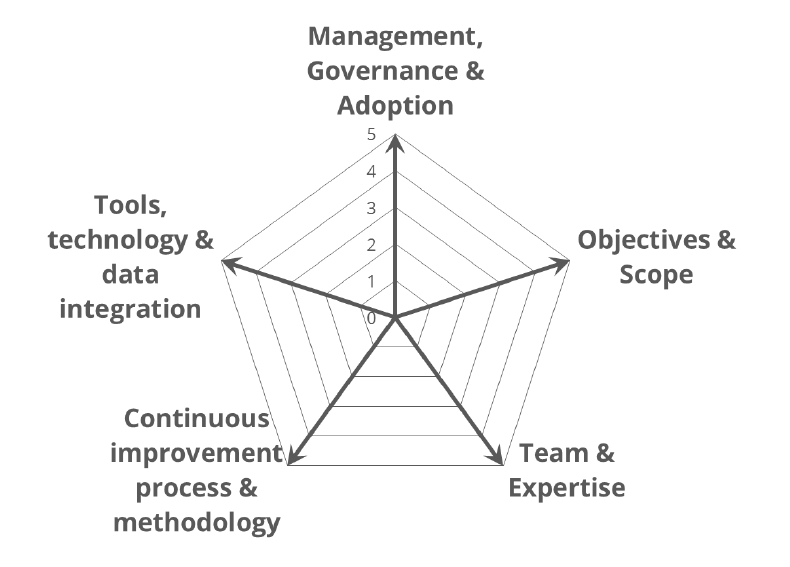
To overcome this issue, Stephane Hamel created the Digital Marketing Maturity Model.
The Data Analytics Maturity Model (DAMM) is a valuable tool organizations use to assess their analytics implementations quickly, identify strengths and weaknesses, and plan for growth effectively.
The DAMM aims to establish balance across all critical areas and help companies gain experience and confidence before moving to higher levels of maturity.
The model offers a structured approach to evaluating critical aspects of analytics implementations, such as data quality, technology infrastructure, analytics processes, and governance frameworks.
The DAMM is an essential guide for organizations to identify areas that require improvement and develop a roadmap to achieve their analytics objectives.
Its efficacy is predicated on its ability to provide a holistic view of analytics implementations, enabling organizations to identify gaps and chart a course for progress.
The Radar chart provided serves as the cornerstone of the process and is instrumental in stimulating discussions, identifying priorities, and enabling growth plans.
Its significance lies in its ability to facilitate a comprehensive analysis of key variables and to provide a visual representation of the relative importance of each element.
This tool allows stakeholders to better understand the underlying factors that impact their business or academic objectives and develop effective strategies to achieve desired outcomes.
Why Digital Analytics is Critical for AI
In today’s world, technology integration and AI digital analytics have become crucial aspects of business competitiveness. Clickstream data is no longer going to suffice.
The utilization of artificial intelligence (AI) to analyze vast amounts of data in a significantly shorter time frame than humans is a valuable opportunity for companies to leverage.
This capability enables companies to uncover impactful results that can be used to their advantage.
However, the performance of AI algorithms depends on the quality of data fed into them.
This makes digital analytics and comprehensive datasets more critical than ever, as companies that provide the best data to AI algorithms will achieve the best results and be the most competitive.
The rise of artificial intelligence has made digital analytics more important than ever for businesses to stay ahead of the competition.
This means that companies must focus on gathering and maintaining high-quality data and work towards implementing more advanced analytics programs.
AI is transforming the business world, and companies must adapt quickly to avoid losing market share to competitors already using AI to their advantage.
It’s all about the quality and completeness of the data in the new world of AI-driven business, and planning appropriately is not only prudent, it is necessary.